Surveillance has come a long way from just watching over things through grainy CCTV footage. Thanks to artificial intelligence, today’s systems are smart, fast, and surprisingly insightful. We are no longer just recording events – we are analyzing them in real time and drawing conclusions that can help organizations stay safer and operate more efficiently.
According to analysts, the AI video surveillance market is expected to jump from around $3.9 billion in 2024 to $12.5 billion by 20301. That’s no coincidence. With the help of computer vision and deep learning, AI can now detect faces, track objects, understand behaviors, and issue alerts almost instantly – and it’s changing how everything from airports to stores stay secure.
The latest generation of analytics tools can automatically monitor different activities and turn surveillance footage into decisions you can actually use. This article dives into how these tools work, where they are used, what they’re good at, and what issues they raise – from technical hurdles to privacy concerns.
What Powers AI CCTV Surveillance Today?
At the core of any AI surveillance setup are two things: cameras and algorithms. Standard IP or CCTV cameras feed video into software that can analyze what’s happening. These tools are built on machine learning models – often convolutional neural networks or, more recently, transformer-based models – that recognize patterns, classify actions, and flag anything unusual.
What’s even more impressive is that many cameras now handle these tasks themselves. They come equipped with built-in GPUs or neural processors that can run analytics right on the device. .That means they can detect a fire hazard or an unauthorized person without needing to send all the footage to a central server – a move that saves bandwidth and makes everything faster2.
Hardware like NVIDIA’s Jetson Orin modules can deliver up to 100 TOPS (trillion operations per second) of AI power in a surprisingly compact form3. Intel chips like the Xeon or Movidius line are also commonly used to process live video streams4. These let surveillance systems “see” and respond in real time with much greater precision than before.
With computer vision, a smart camera can count people, recognize a license plate, or even figure out if someone’s loitering or left a bag behind. This kind of software is what powers many public and private safety systems today.
Edge computing is also playing a huge role. By processing data directly on or near the device (rather than in a data center), AI reduces delay and avoids clogging up the network. Most systems include AI-enabled IP cameras – usually powered via Ethernet – that connect to a video management system (VMS) running analytics software.
Where AI Surveillance Is Actually Used?
AI in surveillance isn’t just for banks or border control anymore. It’s everywhere – from retail chains and airports to city streets and factories. Let’s take a look at some real examples:
- City Safety & Public Transport: Local governments use AI cameras to manage traffic flow, monitor public spaces, and respond to emergencies faster. AI helps transit agencies adjust routes based on passenger volume.
- Retail Stores: Smart cameras help track foot traffic, detect theft, and analyze shopper behavior. Managers can see which displays get attention, when to add staff, and even use license plate recognition to manage parking.
- Airports: Cameras analyze how crowded checkpoints are, so staff can redirect passengers in real time. They also detect unsafe behavior on tarmacs or unattended bags – all while keeping things moving smoothly.
- Corporate and Industrial Settings: Offices use AI to optimize space (e.g., how meeting rooms are used) and automatically grant access to authorized personnel. Factories check if workers are wearing protective gear – if not, they send alerts.
- Law Enforcement & Military: Agencies like the US Department of Defense use AI systems to monitor restricted areas. Some can track suspicious aircraft automatically, outperforming older radar and CCTV systems5.
- Stadiums and Venues: Event organizers rely on real-time crowd analysis to prevent dangerous build-ups or respond to unexpected movement – long before trouble starts.
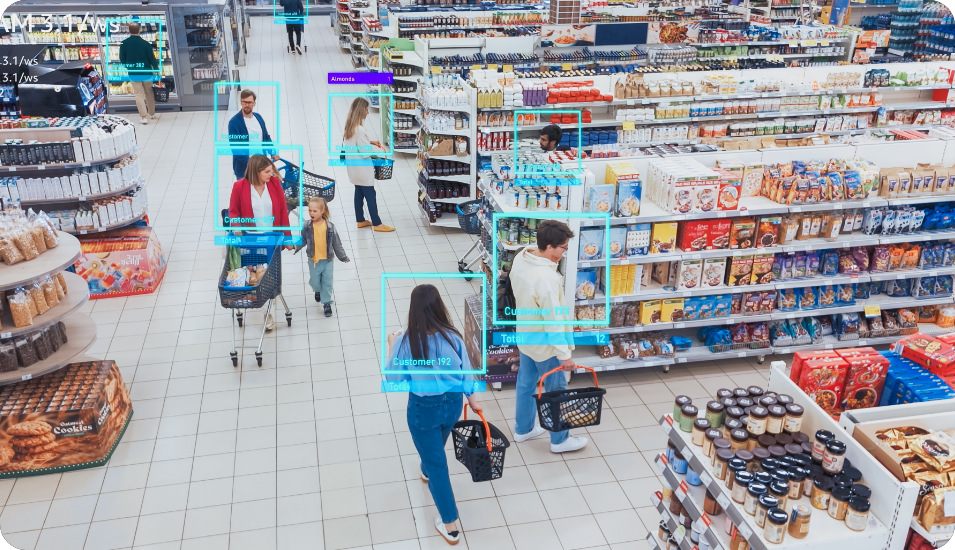

No matter the setting, AI works alongside human guards, helping them spot what they might otherwise miss. These tools turn video into actionable insights that improve both safety and service.
Why AI Surveillance Is So Valuable?
- Speed and Accuracy: AI detects threats – from intrusions to fire – faster than humans, and with more consistency. For instance, it can raise an alarm when someone climbs a fence – long before a guard could notice.
- Saves Time: Staff no longer need to watch footage for hours. AI flags what matters so they can respond faster. AI lets companies capitalize on existing infrastructure – to do more with what they already have.
- Insightful Data: AI doesn’t just protect – it informs. Footage reveals trends in how buildings are used, when crowds appear, or what areas get the most attention. This helps with marketing, planning, and resource management6.
- Easy to Scale: New smart cameras can be added without overwhelming operators. Cloud-based platforms help even small businesses use advanced features without needing a big IT team.
- Ever Improving: Thanks to deep learning, detection is more accurate than ever – even in bad lighting. Self-learning systems reduce false alarms over time7.
AI and video analytics are now among the top growth trends for 2025, with industry partners citing improvements in efficiency, decision-making, and overall safety.
But It’s Not All Perfect – Here’s What Can Go Wrong
- Bad Data = Bad Results: If the AI is trained on flawed or biased footage, it can make mistakes – like missing people in dark clothes or reacting to tree branches as threats.
- Setup Is Complicated: Unlike plug-and-play CCTV, AI systems require alignment between cameras, software, and networks. Devices need updates, and rules must be fine-tuned for each environment.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Ironically, AI can open new attack paths. Hackers might try to hijack video streams or insert fake footage. That’s why encryption, access control, and secure firmware are essential.
- Cost of Hardware: High-performnce systems – especially with lots of high-res feeds – need GPUs, servers, and bandwidth. You’ll need to decide what to run locally and what to send to the cloud.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments are tightening rules, especially around facial recognition and public surveillance. Some cities ban certain uses entirely. The legal gray zone can stall adoption.
- Training Is Required: Your team needs to understand how to respond to AI alerts. IT and security teams must work together, often alongside data scientists, to keep things running smoothly.
What About Privacy and Ethics?
AI video monitoring captures people – and that means privacy is a serious concern. In the EU, GDPR treats video as personal data. If someone can be identified, the footage must be protected like any other sensitive information.
Operators are required to:
- Inform people through clear signs and notices
- Keep records of video use
- Delete footage after a reasonable time
- Report breaches within 72 hours
And with the upcoming EU AI Act, even more controls are coming. Tools that use facial recognition or biometric monitoring will be classed as “high-risk” and need extensive documentation, accuracy guarantees, and ethical oversight8.
There’s growing worry that mass surveillance powered by AI could violate basic rights. The concern isn’t just legal – it’s philosophical: are we creating systems that are fair, transparent, and accountable?
To answer that, organizations must:
- Minimize data collection
- Avoid overreach
- Be transparent about how the system works
- Audit algorithms regularly
- Allow human review of critical decisions9
As Axis Communications points out, trust is essential – customers and citizens need to believe that AI surveillance is being used responsibly, not intrusively10.
Final Word: How to Get AI Surveillance Right
If you’re planning to use AI in your security systems, here’s what to keep in mind:
- Define your goals. Are you trying to stop trespassers? Count customers? Analyze behavior? Choose tools based on that.
- Pick the right software. Some platforms focus on vehicles, others on faces or thermal imaging – choose what fits your scenario.
- Test and tune. Every environment is different. Lighting, angles, and thresholds all matter.
- Keep optimizing. AI improves with feedback. Review alerts and update models as needed.
- Secure everything. Encrypt data, limit access, and stay up to date on patches.
- Train your team. AI works best when humans know how to use it.
- Stay compliant. Follow GDPR, the AI Act, and industry best practices. It will save you from fines and PR disasters later..
As Avigilon puts it, smart use of AI “transforms the way modern businesses approach security” – but only if you know how to use it wisely.
- https://www.globenewswire.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.premioinc.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.securityworldmarket.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.defense.gov/ ↩︎
- https://www.securityworldmarket.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/ ↩︎
- https://www.asisonline.org/ ↩︎
- https://edps.europa.eu/ ↩︎
- https://newsroom.axis.com/ ↩︎